
Need assistance?
Need Assistance? Call Us 0330 058 0630
Did You Know? We Sell Fire Alarm Systems as Complete Kits. Shop Now
20/02/2025 • by Alice P

Aspirating detection is a highly sensitive smoke detection method that actively samples air from a protected area to identify the presence of smoke particles. This advanced fire safety technology uses a network of pipes to draw air into a central detection unit continuously.
The aspirating smoke detection (ASD) system analyses the air samples for the presence of smoke particles, even at extremely low concentrations. This allows for the earliest possible detection of potential fire hazards, often before visible smoke or flames appear.
Aspirating detection systems are designed to provide reliable and accurate smoke detection in a wide range of environments, from small offices to large industrial facilities.

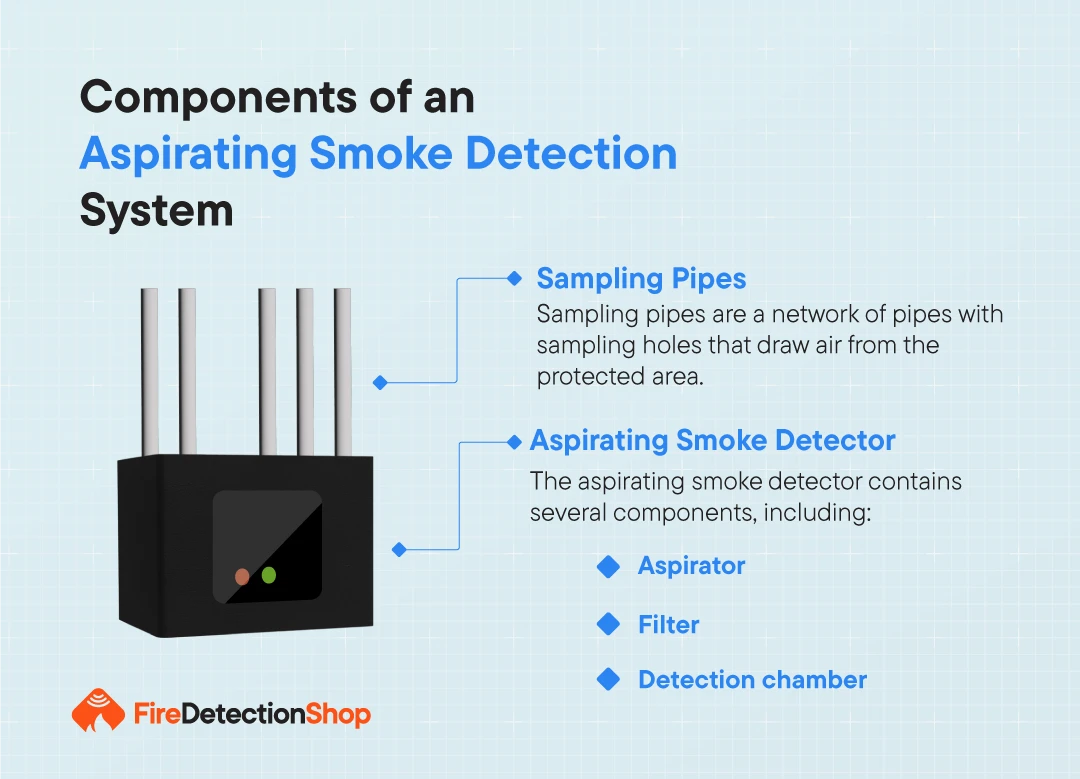
Aspirating fire systems are made up of several key components working in unison to provide early and accurate smoke detection. The main parts include:
Sampling Pipes: A network of pipes with sampling holes that draw air from the protected area.
Aspirator: A fan or pump that continuously draws air through the sampling pipes.
Filter: Filters remove dust and other particles from the air sample to prevent false alarms and protect the detection chamber.
Detection Chamber: The detection chamber is where the air sample is analysed for the presence of smoke particles.
Control Unit: Processes the information from the detection chamber and manages system settings and alarms.
These components work together to provide highly sensitive and reliable smoke detection, often capable of detecting smoke particles long before they become visible to the human eye.
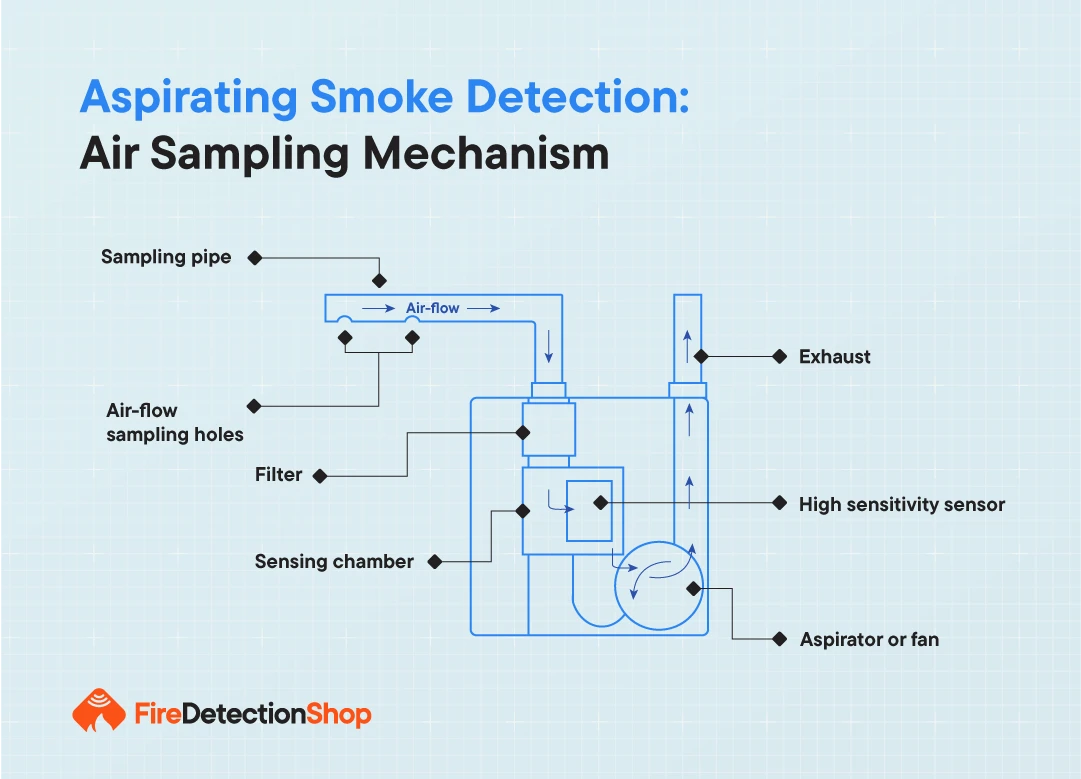
The air sampling mechanism is at the heart of an aspirating fire system. It continuously draws air from the protected area through a network of sampling pipes, which are strategically placed throughout the space.
These pipes contain small, precisely calibrated holes that allow air to be drawn in at regular intervals. The size and spacing of these holes are carefully calculated to ensure even sampling across the entire protected area.
The aspirator, typically a fan or pump, creates the necessary airflow to draw air through the pipes and into the detection chamber. This continuous sampling allows for real-time monitoring of air quality and immediate detection of any smoke particles.
Understanding the operational principles of aspirating systems is crucial for appreciating their effectiveness in fire detection.
Aspirating systems operate on a simple yet effective principle: continuous air sampling and analysis. The process can be broken down into several key steps:
Air is continuously drawn from the protected area through a network of sampling pipes.
The air sample passes through a filter to remove dust and other particles.
The filtered air enters the detection chamber, where it is analysed for the presence of smoke particles.
If smoke particles are detected, the system evaluates the concentration and compares it to pre-set thresholds.
Based on this analysis, the system may trigger an alarm or alert, allowing for early intervention.
This continuous cycle of smoke sampling and analysis allows for real-time monitoring and rapid response to potential fire hazards.
Aspirating systems use advanced technology to detect smoke particles at extremely low concentrations. The detection chamber typically employs one of two methods:
Laser-based detection: A laser beam is directed into the chamber. When smoke particles are present, they scatter the light, which is detected by a highly sensitive photoreceiver.
Cloud chamber detection: The air sample is exposed to a sudden drop in pressure, causing any moisture present to condense around smoke particles, making them more easily detectable.
These methods allow aspirating systems to detect smoke at concentrations far below what would be visible to the human eye, providing the earliest possible warning of a potential fire.
Aspirating fire systems offer several significant advantages over traditional smoke detection methods. The two main advantages these systems offer are their extremely early warning capabilities and their versatility in a number of environments, particularly locations with high airflow and extremely high ceilings.
The primary advantage of aspirating fire systems is their early warning capabilities. These systems can detect smoke at extremely low concentrations, often long before a fire becomes visible or traditional detectors would activate.
This early detection is crucial in minimising potential damage and ensuring the safety of occupants. In many cases, aspirating systems can detect a fire in its very early stage, allowing for intervention before the fire can spread or cause significant damage.
Moreover, the continuous monitoring provided by aspirating systems allows for the detection of slow, smouldering fires that might go unnoticed by traditional detectors for extended periods.
Aspirating fire systems demonstrate remarkable versatility, making them suitable for a wide range of environments. They are particularly effective in:
Large, open spaces: Such as warehouses or atria, where traditional detectors might struggle to detect smoke quickly.
High-airflow areas: Like data centres or clean rooms, where smoke can be rapidly dispersed.
Harsh environments: Including areas with high levels of dust or extreme temperatures, where traditional detectors might fail or produce false alarms.
Aesthetically sensitive locations: Such as historic buildings or museums, where the sampling pipes can be discreetly installed.
This versatility makes aspirating systems an ideal choice for complex or challenging environments where fire detection is critical.
When compared to traditional smoke detection methods, aspirating systems offer several key advantages:
Feature | Aspirating Systems | Traditional Detectors |
Sensitivity | Extremely high, can detect invisible smoke particles | Lower, typically require visible smoke |
Response Time | Very fast, often minutes or hours before traditional detectors | Slower, requires more developed fire |
False Alarm Rate | Low, due to advanced filtering and analysis | Higher, especially in challenging environments |
Coverage | Large areas with a single system | Multiple detectors are required for large areas |
Maintenance | Centralised, easier to maintain | Individual detectors require separate maintenance |
Versatility | Suitable for a wide range of environments | May struggle in certain conditions |
While traditional detectors remain a viable option for many applications, aspirating systems offer superior performance in terms of early detection, reliability, and versatility.
Installing an aspirating fire system requires careful planning and execution to ensure optimal performance. Key considerations include:
System Design: The layout of sampling pipes and hole locations must be carefully calculated to ensure even coverage and appropriate sensitivity throughout the protected area.
Environmental Factors: Factors such as airflow patterns, temperature variations, and potential sources of dust or contamination must be taken into account during installation.
Integration: The system should be integrated with existing fire safety and building management systems for comprehensive protection.
Accessibility: While sampling pipes can be installed discreetly, the central detection unit should be easily accessible for maintenance and testing.
Compliance: Installation must comply with relevant local and national fire safety regulations and standards.
Proper installation by qualified professionals is crucial for ensuring the system's effectiveness and reliability.
For more information on aspirating smoke detection systems, such as VESDA, please contact our team of specialists by calling 0330 058 0630 or emailing [email protected]
11/01/2021 • by Lynsey B